Service
Product Search

Post-translation Modification(PTMs)
Post-translational modification of a peptide has been linked to many biological functions and cellular processes, such as protein degradation, signaling and regulatory processes, regulation of gene expression, and protein-protein interactions.
Crefu Peptides has a extensive experience in the synthesis of below listed post-translationally modified peptides:
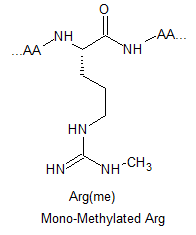
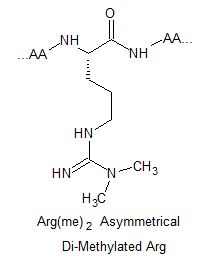
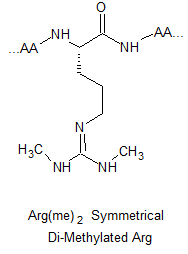
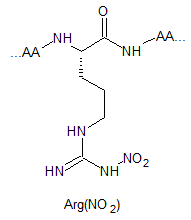
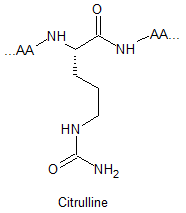
Arginine Methylation Peptide Modifications
Arginine methylated are involved in a number of different cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation, RNA metabolism and DNA damage repair. Their respective structures are shown as below:
Arginine Methylation Peptide Modifications
Arginine methylated are involved in a number of different cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation, RNA metabolism and DNA damage repair. Their respective structures are shown as below:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
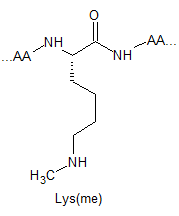
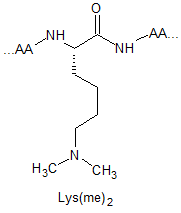
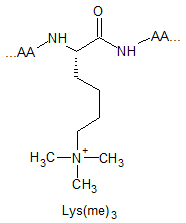
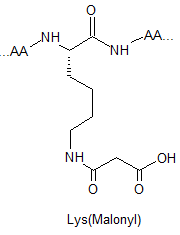
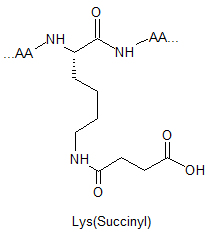
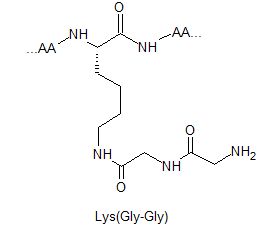
Lysine Methylation Peptide Modifications
Lysine methylation is restricted to a subset of proteins and catalysed by highly specific methyltransferases that can generate mono-, di-, and trimethylated lysines. These modifications result in changes in protein : protein interactions, chromatin structure and gene expression. Their respective structures are shown as below:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Glycopeptides Modifications
Glycosylation is one of the most common post-translational modifications of proteins, with significant effects on protein folding, conformation, distribution, stability and activity.
N-linked glycosylation
N-linked glycosylation are covalently attached to protein at asparagine (Asn) residues by an N-glycosidic, and is important for both the structure and function of some eukaryotic protein.
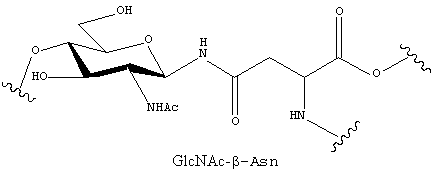 |
O-linked glycosylation
O-Linked glycosylation are form by a linkage between an amino acid hydroxyl side chain (usually from serine or threonine) with the glycan. The majority of O-linked glycans take the form GlcNac-β-Ser/Thr or GalNac-α-Ser/Thr.
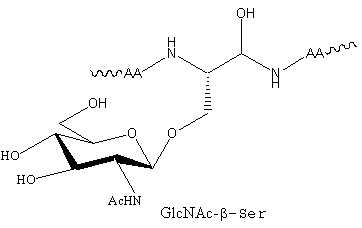 |
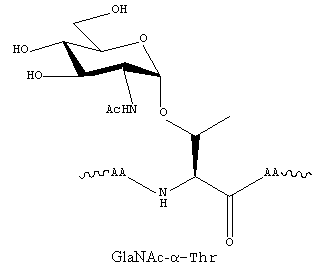 |
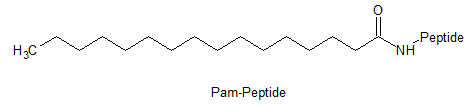
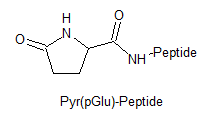
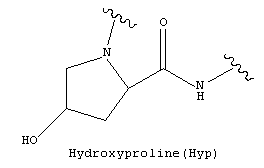
Other PTMs
Myristoylation, Palmitoylation, Pyroglutamate(Pyr), Proline hydroxylation(Hyp).
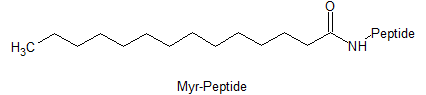 |
 |
 |
 |