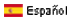C-terminal & N terminal modifications
C-termnal |
Structure Show | N-terminal | Structure Show |
|
Aldehyde
|
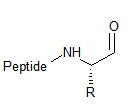 |
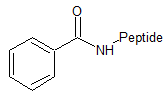
Benzoyl (Bz)
|
 |
| Alcohols |  |
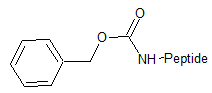
CBZ
(Benzyloxycarbonylation)
|
 |
|
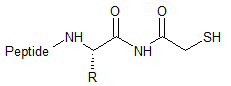
Cysteamide
(Mercaptoacetamide)
|
 |
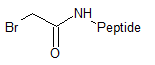
Bromoacetyl (Br-Ac)
|
 |
|
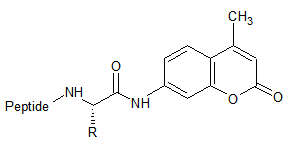
AMC
7-amino-4-methylcoumarinyl |
 |
Formylation | 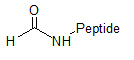 |
|
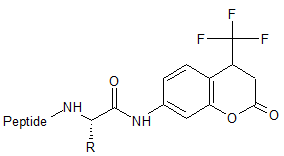
AFC
7-amino-4-(trifluoromethyl)-2-benzopyrone
|
 |
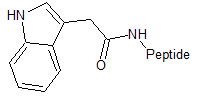
3-Indolylacetic acid
|
 |
|
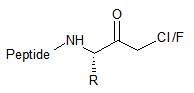
CMK/FMK
Chloro(fuoro)-methylketones
|
 |
Mpa
(3-Mercaptopropyl) |
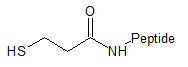 |
|
Ester (OMe/ OEt)
|
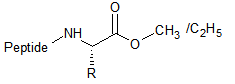 |
Succinylation
|
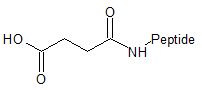 |
|
Hydrazide
|
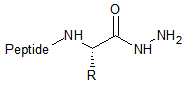 |
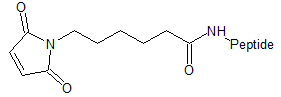
MCA 6-Maleimidohexanoic acid
|
 |
|
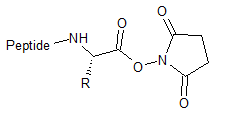
OSU
|
 |
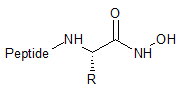
Hydroxamic acid
|
 |
|
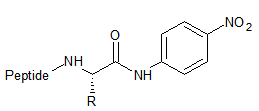
pNA (p-Nitroanilide)
|
 |
Thioester
|
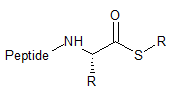 |
Aldehyde peptide: peptide aldehydes have the inhibition properties towards various enzymes. Furthermore, peptide aldehydes
are of great interest for peptide backbone modification or ligation reactions.(J Pept Sci. 2007 Jan;13(1):1-15. Moulin A1, Martinez J, Fehrentz JA )
CMK/FMK labeled peptide: Peptide chloromethylketones (CMK) are very potent and irreversible inhibitors of serine proteases.
Availability depending on peptide sequence.
Ester (OMe/ OEt) : For structure-activity relationships (SAR), removal of charge, prodrug.
p-Nitro-Aniline: a chromogen used as colorimetric enzyme substrate in many standard enzyme assays in cuvettes. Excitation
maximum is 410 nm.
Formylated peptide: The formyl peptide receptor (Fpr) family is well known for its contribution to immune defense against
pathogens in human and rodent leukocytes.
Cholesterol conjugated peptide: the cholesterol-conjugated compounds are effective inhibitors of infectivity and membrane
fusion. Cholesterol can be conjugated to a peptide via a N- or C-terminal inserted cysteine.
|
Cholesterol conjugated at peptide N-terminal |
Cholesterol conjugated at peptide C-terminal(via Cys) |
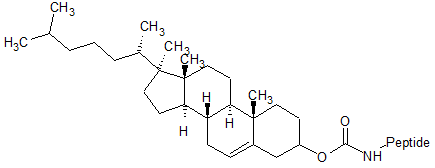 |
 |
Fatty acid conjugated peptides: Fatty acid conjugated peptides can be used for antibacterial activity or eukaryotic cell toxicity and
so on. fatty acids like Caprylic acid (C8), Capric acid (C10), Lauric acid (C12), Myristic acid (C14), Palmitic acid (C16) or Stearic
acid (C18) etc general conjugated on the peptide N-terminal or on the C-terminal via lysine side chain.