Service
Product Search

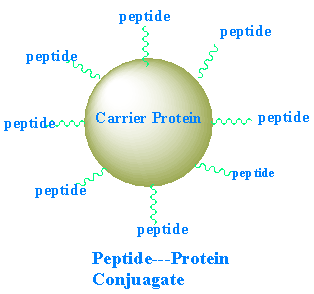
Peptide Conjugate to Carrier Proteins (KLH, BSA and OVA )
Short peptides are usually too small to elicit a sufficient immune response, therefore, it is necessary to conjugate
the peptide to a larger carrier protein to promote a good immune response and to generate high levels of specific
antibody. Crefu Peptides provide below listed most commonly used carrier protein for peptide conjugates:
KLH (keyhole limpet hemocyanin, MW 4.5x105 - 1.3x107 Da) is a copper-containing protein and isolated from Megathura crenulata, and generally is the first choice used carrier protein because of its high immunogenicity. KLH conjugated peptides often have limited solubility in water due to its size and structure, however, this does not affect its immunogenicity and cloudy solutions can be used for immunizations.
BSA (bovine serum albumin, MW 67x103 Da) is a popular carrier protein for weakly antigenic compounds because of the high number of accessible Lys residues for conjugation. BSA is more water-soluble than KLH because it is smaller; therefore, it is used more commonly in immunoassays. However, because BSA is commonly used to block nonspecific binding sites in antibody-based assays BSA conjugates should not be used for immunization if the end-point assay system uses BSA. This is because if antisera against peptide-BSA conjugates are used in these assays, false positives are common because the sera used also contain antibodies against BSA.
OVA (ovalbumin, MW 45x103) is a protein isolated from chicken eggs. It is often used as a control carrier protein to verify that antibodies are specific for the target peptide rather than the carrier protein (e.g. KLH/BSA).
Short peptides are usually too small to elicit a sufficient immune response, therefore, it is necessary to conjugate
the peptide to a larger carrier protein to promote a good immune response and to generate high levels of specific
antibody. Crefu Peptides provide below listed most commonly used carrier protein for peptide conjugates:
KLH (keyhole limpet hemocyanin, MW 4.5x105 - 1.3x107 Da) is a copper-containing protein and isolated from Megathura crenulata, and generally is the first choice used carrier protein because of its high immunogenicity. KLH conjugated peptides often have limited solubility in water due to its size and structure, however, this does not affect its immunogenicity and cloudy solutions can be used for immunizations.
BSA (bovine serum albumin, MW 67x103 Da) is a popular carrier protein for weakly antigenic compounds because of the high number of accessible Lys residues for conjugation. BSA is more water-soluble than KLH because it is smaller; therefore, it is used more commonly in immunoassays. However, because BSA is commonly used to block nonspecific binding sites in antibody-based assays BSA conjugates should not be used for immunization if the end-point assay system uses BSA. This is because if antisera against peptide-BSA conjugates are used in these assays, false positives are common because the sera used also contain antibodies against BSA.
OVA (ovalbumin, MW 45x103) is a protein isolated from chicken eggs. It is often used as a control carrier protein to verify that antibodies are specific for the target peptide rather than the carrier protein (e.g. KLH/BSA).
 |
Generally, which kinds of conjugation chemistry used depend on the provided antigen peptide sequence.
|
Reaction Site
|
Chemistry |
Comments |
| Free-NH2 group | Glutaraldehyde | ①Recommend N-terminal free NH2, avoid Lys or a Pro N-terminus in the internal sequence if possible ②Antigen peptide sequence comes from the C-terminal or in- ternal region of the protein |
| Free-COOH group | EDCI | ①Recommend C-terminal free COOH, avoid Glu or Asp in the internal sequence if possible ②Antigen peptide sequence comes from the N-terminal or internal region of the protein |
| Free-SH group | MBS/SMCC | Commonly used approach, usually via the addition of an extra Cys to the sequence at either the N-or C-terminus |